Google’s DeepMind team has developed a new system for teaching robots novel tasks. The system, called Robotics Transformer 2 (RT-2), the first vision-language-action (VLA) model for robot control which is based on a transformer architecture, which is a type of neural network that is well-suited for natural language processing tasks. RT-2 is able to learn from a small number of demonstrations and generalize to new tasks.
RT-2 is a versatile AI system that can learn and adapt to new situations. It can learn from multiple data sources, including the web and robotics data, to understand both language and visual input. This allows RT-2 to perform tasks that it has never encountered nor been trained to perform.
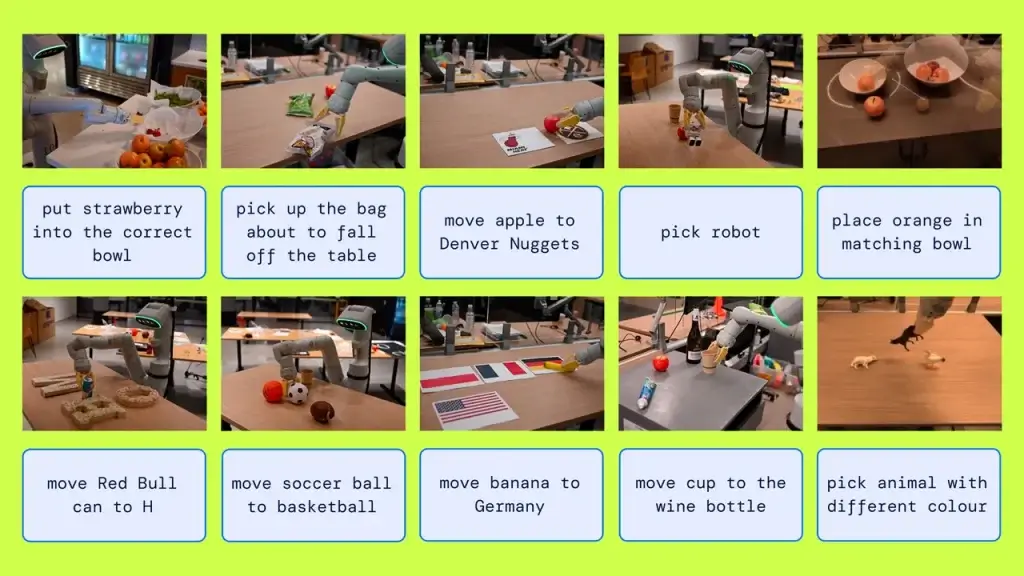
References image from Google DeepMind
Adapted Existing Model
DeepMind team redesigned Pathways Language and Image Model (PaLI-X) and Pathways Language Model Embodied (PaLM-E) which are two existing models, to train RT-2.
PaLI-X assists the model process visual data, trained on massive amounts of images and visual information with other corresponding descriptions and labels online. With PaLI-X, RT-2 can recognize different objects, understand its surrounding scenes for context, and relate visual data to semantic descriptions.
PaLM-E assists RT-2 interpret language, so it can easily understand instructions and relate them to what is around it and what it’s currently doing.
These two models enable a robot to understand language and visual data and subsequently generate the appropriate actions it needs.
DeepMind’s Distinguished Scientist and Head of Robotics, Vincent Vanhoucke, said that RT-2 “shows improved generalization capabilities and semantic and visual understanding beyond the robotic data it was exposed to.” He also said that the system “allows robots to effectively transfer concepts learned on relatively small datasets to different scenarios.”
One of the challenges of teaching robots novel tasks is that robots need to be able to understand the context of the task. For example, if a robot is asked to “throw away the trash,” it needs to be able to understand that the trash is an object that needs to be disposed of. RT-2 is able to do this by learning the semantic meaning of words and phrases.
RT-2 has been tested on a variety of tasks, including picking and placing objects, opening drawers, and sorting objects. The system has been shown to be able to learn these tasks from a small number of demonstrations and generalize to new tasks.
Vanhoucke said that RT-2 is “a significant step forward in the development of robots that can learn and adapt to new situations.” He said that the system “has the potential to make robots more useful and versatile in a wide range of settings.”
RT-2 possible applications:
- It can learn from a small number of demonstrations. This means that robots can be trained more quickly and efficiently.
- It can generalize to new tasks. This means that robots can be used in a wider range of settings.
- It can understand the context of tasks. This means that robots can be more efficient and effective at completing tasks.
RT-2 has the potential to revolutionize the way robots are used. It could make robots more useful and versatile in a wide range of settings. For example, RT-2 could be used to train robots to perform tasks in warehouses, factories, and hospitals. It could also be used to train robots to help people with disabilities.
The development of RT-2 is a significant step forward in the field of robotics. It is a promising new technology that has the potential to make robots more useful and versatile.